Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): How to Manage Procurement Efficiently?
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)is the optimal order quantity for a specific product. Knowing how much to order, chain managers can:
- avoid over-ordering products;
- minimize the cost of product storing;
- prevent out-of-stocks;
- satisfy the demand of customers and minimize losses in sales value;
- optimize inventory management.
!Have you ever wondered how much the chain loses due to incorrectly calculated order sizes?
- stores lose about 7% of their sales value due to a shortage of products;
- excess product stocks increase the cost of their maintenance by 20%;
- due to improperly configured purchasing logistics, the chain loses up to 10% ofprofits.
The calculation and analysis of EOQ will allow you to balance the product stock that will ideally cover the existing demand. So you can solve two problems: 1) prevent a shortage of goods (out-of-stocks); 2) avoid surplus goods.

EOQ: 3 factors are should be considered
The calculation of the economic order quality requires the definition of 3 parameters:
- annual demand for products,
- ordering costs;
- product storage costs.
Annual demand for products
Demand is the number of products that customers buy in your stores. For EOQ, you need to predict sales qty for the year. To do this, one should take into account both historical data and many additional external factors (inflation, seasonality of purchases, etc.). Using the BES analytics platform and included Machine Learning technologies (LightGBM model), you are guaranteed to get the most accurate demand forecasts with desired detail.
Order costs
Order costs are the cost of a separate order of products for the chain. This option includes various costs connected with:
- ordering and delivery of products: the cost of products and transportation costs;
- search for a supplier;
- processing of payments on invoices;
- insurance;
- wages of employees who carry out the order;
- unexpected and impromptu payments affecting an incoming order.
Maintenance costs
Maintenance costs arise in the chain as soon as the products enter the warehouse. They include:
- the cost of renting and maintaining storage facilities;
- wages of warehouse workers;
- packaging costs;
- losses due to improper storage of products, obsolescence, etc.
EOQ: calculation formula
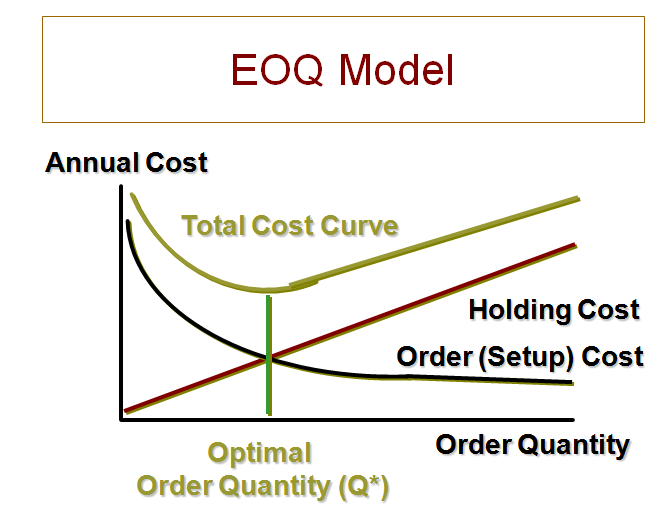
The calculation of the economic order quality should take into account the following conditions:
- The EOQ calculation methodology assumes that annual demand is precisely predictable and constant.
- The calculation does not take into account the product stocks. When re-ordering, the remaining products are considered zero or completely sold.
- Restocking is assumed to occur immediately after a reorder. Delivery time is not included.
- Savings from wholesale purchases and provided supplier discounts are not missed in the calculation.
- EOQ is focused on solving the maximization-minimization problem. The main task is to maximize the quality of ordered products, minimizing the cost of ordering and storing them.
The formula for calculating EOQ:
EOQ = √(2DS/H),
where:
- D - annual demand for the product in units
- S - cost for ordering a unit of product
- H - the cost of storing a unit of product per year
- Q - economic order quantity in units
As mentioned earlier, applying the Economic Order Quantity formula is very simple. The work mainly consists of collecting, storing, aggregating, and analyzing the data necessary to calculate the EOQ variables. And here we offer the best tool - BES analytical platform for retailers with convenient modules for customizing your data and smart artificial intelligence tools.
EOQ: calculation example
Consider an example of calculating EOQ.
The chain owner wants to optimize their logistics system by calculating the economic order quantity for product A.
Problems faced by the chain:
- managers constantly change the size of orders, which led to significant stocks of product A in the warehouse;
- the chain meets with large costs for their storage;
- it is difficult for management to estimate the release time of cash invested in inventory.
It is known that the product is sold annually in the amount of 3000 units (demand D). To store it, the chain spends $10 (H), and the cost of the order is $7 (S).
EOQ = √(2DS/H) = √(2*3000*7/10) = 65 units
For the chain, the minimum stock of product A, which must always be in stock, is 65 units. This amount of products will satisfy existing demand and avoid excess and additional storage costs.
Factors that affect EOQ
EOQ is a convenient and easy way to plan product inventory, but its effectiveness depends on many factors:
- Re-order and stocks. If the stock of products is too large or too small, then it is necessary to analyze their cause and adjust the EOQ accordingly.
- Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ). If suppliers require minimum orders, then the EOQ will be adjusted up or down.
- Times of delivery - sometimes lead times are long and the EOQ runs out before the next replenishment. You may need an additional stock that exceeds the EOQ level as a safety stock.
- Unexpected rise or fall in demand - Unexpected upward changes in demand run out of stock faster than planned. The EOQ level should be adjusted accordingly to account for such deviations in sales.
- Discounts - receiving discounts from suppliers may result in the supply of additional items. This ultimately reduces EOQ for certain periods as you may not always need the quantity ordered.

Conclusions
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is an effective tool for inventory management. If this indicator is neglected, the chain will deal with surpluses of products during a period of low demand and product shortages during a period of increased demand.
Any of the above situations have negative consequences for the company:
- too large inventories lead to the "freezing" of funds in products;
- stock shortages are the main cause of lost sales.
Therefore, the correct calculation of EOQ effectively manages inventory and maximizes chain revenue. With built-in tools on the BES platform, you can easily predict and calculate the right metrics needed to analyze the economic order quantity (EOQ).
 Co nowego?
Co nowego?




 Nie potrzebna karta bankowa!
Nie potrzebna karta bankowa!