Pricing is one of the most important aspects of retailing, affecting product demand, competitiveness and profitability of the business. Price should cover costs, ensure profit and be competitive in the market....
Principles of pricing
The basic principles of pricing include:
- Cost is the total of all the costs of its production or purchase. It includes:
- Direct costs (purchase of raw materials, components, labor remuneration of employees);
- Indirect costs (logistics, rent, utility payments);
- Administrative costs and marketing.
- Market conditions - supply and demand, seasonal factors, inflation and industry trends are taken into account.
- Pricing strategy of the company - selected depending on the positioning of the business: premium, medium or budget segment.
- Competitive environment - analyzing competitors' prices helps to determine which pricing policy to choose.
- Value to the consumer - the price of the product should reflect its value in the eyes of the buyer.
How to calculate the price of goods
To calculate the price of products, you can use the following formula:
Price = cost price + fixed costs + variable costs + advertising costs + profits
All costs need to be summarized and divided by the planned number of merchandise to be sold.
Price per unit = (cost of sales + fixed costs + variable costs + advertising costs + profit) / number of products
Deciphering the components of the formula:
- Cost of sales - cost of raw materials, raw materials, production and delivery of products.
- Fixed costs - rent, utilities, employee salaries.
- Variable costs - depend on the volume of sales, such as packaging, transportation, logistics.
- Advertising costs - marketing costs to promote the product.
- Profit - the desired benefit included in the price.
Example calculation:
Let's assume that the cost price of a unit of goods - 200 UAH,
- fixed costs - 50 000 UAH per month,
- variable costs - 30 UAH per unit,
- advertising budget - 20 000 UAH per month,
- sales plan - 1000 units per month,
- desired profit - 100 000 UAH.
Calculation:
Price = (200 × 1000 + 50 000 + 30 × 1000 + 20 000 + 100 000) / 1000
Price = (200 000 + 50 000 + 30 000 + 20 000 + 100 000) / 1000
Price = 400,000 / 1000
Price per unit = 400 UAH
Thus, to cover all costs and get the planned profit, you need to set a price of 400 UAH per product.
How to set the price of products taking into account market conditions
To determine the price it is necessary to analyze the market:
- Study competitors - what prices are set for similar merchandise?
- Evaluate demand - high demand allows you to set a higher price.
- Understand the price sensitivity of the audience - some customers are willing to pay more for quality or brand.
The minimum price of a product is determined based on the cost of production. If the price is lower than this value, the business will be unprofitable. The optimal price should take into account not only costs, but also margins and competitor opportunities.
How to determine the optimal markup
Themarkupis the percentage that is added to the cost price to make a profit.
The markup formula is:
Markup = (Selling Price - Cost of Sales) / Cost of Sales × 100%
Elasticity of demand and its effect on price
Elasticity of demand shows how a change in price affects the volume of sales.
- Highly elastic demand: a decrease in price increases sales (e.g. electronics, clothing)
- Low elastic demand: a change in price has little effect on sales (e.g., drugs, gasoline)
Elasticity of demand formula:
E = (% change in sales volume) / (% change in price)
If E > 1, the product is elastic, if E < 1, it is inelastic.
Pricing methods
There are different pricing methods that can be applied depending on the goals of the company.
1. Cost method
This method is based on the cost of goods. A fixed percentage of profit is added to it. It is easy to use but does not take into account competitors and demand.
Example: If the cost of goods - 800 UAH, and a markup of 40%, the price will be:
800 + (800 × 0,4) = 1120 UAH.
2. Value-based pricing
This method takes into account the value of the product for the consumer. For example, if the product has unique characteristics, its price may be higher.
Example: A smartphone of a premium brand may cost 70,000 UAH even if its cost price is 25,000 UAH, as customers are willing to pay for the brand and innovation.
3. Competitive pricing
Prices are set based on the analysis of competitors. You can choose:
Price below the market - to attract customers.
Price at the level of competitors - to maintain parity.
Above market price - if there is a competitive advantage.
Example: If competitors have a similar product costs UAH 1500, the company can set the price at UAH 1400 to attract customers.
4. Dynamic pricing
It is used in e-commerce and retail. The price varies depending on demand, time of day, the balance of goods.
Example: Stores increase the price of seasonal items closer to the holidays as demand increases.
5. Psychological pricing
The techniques like “price trap” (99 UAH instead of 100) or creating the effect of scarcity (“3 pieces left!”) are used.
6. Demand-based pricing
It is determined how sensitive the buyer is to price changes. For example, if the price of goods will increase by 10%, but demand will not decrease - this is a signal to increase the markup.
7. Recommended Retail Price (RRP).
This is a strategy in which the manufacturer sets a single price level for all sellers. It helps to avoid dumping and maintain brand value.
Demand for a product and factors affecting price
Demand for a product is the most important factor in pricing. It is influenced by:
- Seasonality - demand may increase during certain periods (e.g., New Year merchandise).
- Quality and uniqueness - exclusive goods can be sold more expensive.
- Marketing and promotion - active advertising can stimulate demand.
What pricing models are commonly used in retail and digital businesses?
Depending on business type, companies may use different pricing models:
- Freemium pricing – basic version is free, advanced features are paid (common in SaaS and digital products).
- Tiered pricing – multiple price levels for different customer segments.
- Flat-rate subscription – fixed recurring fee for defined services.
- Bulk (volume) pricing – lower unit price for larger purchases (common in B2B and wholesale).
- Market-based pricing – price set according to competitor positioning and demand conditions.
Choosing the correct model depends on customer behavior, competition, and strategic goals.
Mistakes in price formation
- Ignoring competitors - if the price is higher without visible advantages, customers will go to competitors.
- Overcharging - high margins can reduce demand.
- Lack of flexibility - prices should be adjusted depending on the market situation.
- Failure to take seasonality into account - for example, lowering prices on winter clothes in summer helps to sell off leftovers.
- Ignoringanalytics- without analyzing data, profitable opportunities can be lost.
How to automate pricing
To effectively manage pricing, it's important to utilize analytical tools. One such tool is the “Price Recommendations” report in Datawiz BI service.
This report helps you to:
- Identify products worth changing prices for in individual stores in the chain.
- Track the impact of price changes on profits.
- Forecast sales after price adjustments.
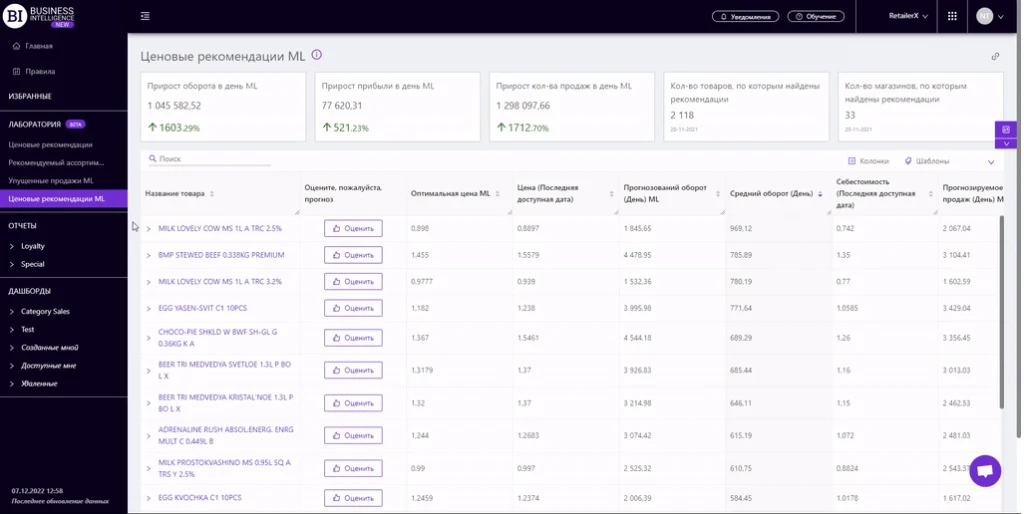
This toolallows you to avoid errors in pricing and maximize profitability.
Proper pricing is not just a markup on the cost price, but a whole strategy that takes into account demand, competitors and market conditions. The use of analytics, such as Datawiz, helps to find optimal prices and increase business profitability.
FAQ: Product Pricing Strategy and Calculation
What is a product selling price?
A product selling price is the final amount a customer pays for a product or service. It must cover all production and operational costs while ensuring profitability and remaining competitive in the market. The selling price is influenced by costs, demand, perceived value, and competitor pricing.
How do you calculate the average selling price (ASP)?
The average selling price (ASP) helps benchmark your product against the market.
Formula:
Average Selling Price = Total Revenue ÷ Number of Units Sold
For example, if revenue is 2,000,000 UAH from selling 4,000 units:
ASP = 500 UAH
This metric helps you understand market positioning and pricing competitiveness.
What is target costing and when should it be used?
Target costing is a pricing method where the market price determines the maximum allowable production cost.
Instead of adding profit to cost, businesses calculate backwards:
Target Cost = Market Price − Desired Profit
For example:
If the market price is 1000 UAH and desired margin is 40% (400 UAH),
then the maximum production cost should not exceed 600 UAH.
This method is especially effective in competitive markets where price sensitivity is high.
What is cost-plus pricing?
Cost-plus pricing involves adding a fixed profit percentage to total costs.
Example:
If total cost per unit is 500 UAH and target margin is 30%:
Selling Price = 500 + (500 × 0.30) = 650 UAH
This method is simple and widely used for physical goods but should be validated against market demand.
How often should pricing be reviewed?
Pricing should not be static. In modern retail environments, prices should be reviewed regularly based on:
Changes in demand
Competitor price adjustments
Inflation and cost fluctuations
Conversion rates
Customer feedback
New features or product improvements
Quarterly reviews are recommended, while dynamic categories may require weekly analysis.
How do you determine the right profit margin?
There is no universal “correct” margin, but typical benchmarks include:
Physical retail products: 30–60%
SaaS and digital products: 70–90%
Wholesale distribution: 15–40%
Margin levels depend on:
Industry standards
Brand positioning
Business maturity
Competitive intensity
Cost structure
Higher differentiation allows higher margins.
What is dynamic pricing and when should it be used?
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real time based on:
Demand fluctuations
Inventory levels
Time of day
Seasonality
Competitor price monitoring
It is widely used in ecommerce, retail chains, airlines, and hospitality. Dynamic pricing maximizes revenue and improves inventory turnover.
What factors influence product pricing in 2026?
Modern pricing decisions are increasingly influenced by:
High price transparency due to AI comparison tools
Faster competitor price changes
Rising customer acquisition costs
Increased consumer price sensitivity
The need to balance growth and profitability
This makes pricing strategy more data-driven and analytical than ever before.
What is the minimum price a business can set?
The minimum price is determined by the total cost per unit. Pricing below total cost leads to losses unless it is a deliberate short-term strategy (e.g., penetration pricing or inventory liquidation).
What is penetration pricing and price skimming?
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to quickly gain market share.
Price skimming involves setting a high initial price and lowering it gradually over time.
Both strategies are used depending on product lifecycle and competition intensity.
Why is pricing validation important?
Even if a price is correctly calculated based on cost, it must be validated against:
Competitor prices
Customer willingness to pay
Perceived product value
Market expectations
Pricing should be tested and optimized continuously using analytics and performance data.
 Novedades
Novedades





 ¡No se necesita tarjeta bancaria!
¡No se necesita tarjeta bancaria!